Web3 crash course: The essentials
And why UX Designers should care.

Taylor Green
Dec 30, 2021
7
min read
If you have been wondering what Web3 is and how you might harness its power as a UX or Product Designer, then you have come to the right place. Let’s start with some background information.
Web2 vs Web3
Web2 (early 2000s — present) is the era of tech giants and social platforms. Users create and consume content in increasing quantities, and mega-powerful tech companies supply the platforms. These companies act as the middleman between the consumer and the content.
Web3 (2020+) is the era of ownership. Users have the ability not only to create and consume content but to own their content as well. This ownership comes in the form of tokens. Web3 is built on peer-to-peer networks of computers that communicate with each other, which avoids the need for a middleman.
What is blockchain?
In simple terms — “Blockchains store a history of transactions between parties on a forum that can be accessible by anybody.” (web3.university)
Every block consists of a list of transactions, a hash (long string of random characters) for that particular block, and the previous block’s hash. Blocks are linked to the previous block, which forms a chain (aka blockchain). The only way a block can be added to the blockchain is if the other nodes agree.
In order for the nodes to process transactions, they must reach consensus. Consensus algorithms are a core component of the architecture that makes it possible to process transactions without a middleman. The consensus is a decision-making process for the group of nodes active on the network.
There are a couple of popular mechanisms for how nodes reach consensus:
Proof of Work (Bitcoin uses this)
Proof of Stake (requires less energy, Ethereum is transitioning to this)
This post won’t dive into the details of these, but I recommend checking out this article if you want to learn more.
What makes blockchain valuable?
Bitcoin was the first widespread use of blockchain technology. The blockchain concept introduced in the design of Bitcoin has since been used to build general-purpose smart contract platforms, which enable applications like DeFi, NFTs, etc.
What makes a blockchain so powerful are these key properties:
1. Decentralized — no governing authority over transactions. The network is maintained by a group of nodes.
2. Immutable — once the transaction is committed, it cannot be changed or altered.
3. Open — anyone can view a transaction.
These three qualities are what make something built on a blockchain, such as Bitcoin, qualitatively different from a traditional bank or centralized system to store money. Blockchain technology allows for enhanced security and faster settlements.
More importantly, it minimizes the need for trust — The idea is that you don’t have to rely on trusting someone/something because you can verify it yourself via the blockchain.
Bitcoin vs. Ethereum
Both Bitcoin and Ethereum are built using blockchain technology. However, they have fundamental differences that make each of them distinctly valuable.
Bitcoin’s sole purpose was to be a decentralized network that allowed people to transfer and exchange value. It was created to be an alternative to traditional fiat money backed by a central authority (aka the government). Its primary use case today is a store of value.
Whereas Bitcoin has a single purpose, Ethereum has several purposes. It was built in 2015, after Bitcoin, and its main intention is to be an open-ended decentralized software platform. Ethereum is flexible and allows developers to create decentralized applications (dapps) via smart contracts.
It’s important to be aware that Bitcoin and Ethereum are inherently different ideas. Ethereum takes blockchain one step further than Bitcoin does. Ethereum can be thought of as an economy and Ether can be thought of as the currency that fuels that economy.
The purpose of the Ethereum ecosystem has multiple use cases, which we will dive into below:
#1 Dapps
Dapps stand for decentralized applications and are similar to the normal apps we use every day. The main difference is in the back-end. Dapps run on a blockchain and can be thought of as a business that is built using blockchain technology via the Ethereum platform.
The backend of these apps is different than an app we might use, such as Spotify, however, to the user the UI essentially looks the same.
Similar to when you are browsing the app store and see a variety of apps for different uses, Dapps can also take on different forms, such as games, social media, trading platforms, etc.
Check out dapp.com if you are interested in browsing what Dapps are out there.
#2 DAOs
A DAO stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization. As the name implies, this just means it is an entity with no central authority, aka no CEO or individual. They are effectively a new method for how businesses can be run.
So who is running the DAO? The members of the DAO are the ones who collectively run and manage the organization.
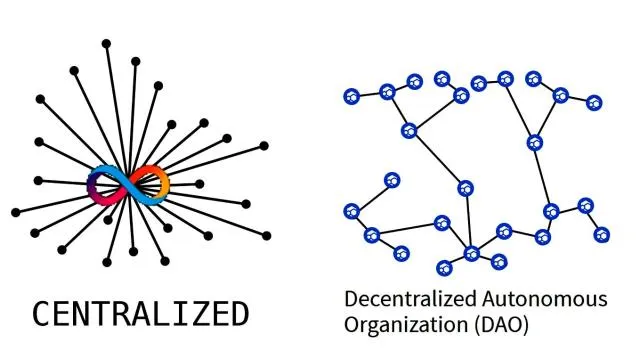
https://bitcoinke.io/2021/07/a-look-at-daos/
DAOs have a similar back-end to Dapps, and can be built on top of Ethereum. DAOs operate via smart contracts that define the rules of the organization. Decisions get made by members of the DAO through the submission of proposals and a group voting system using tokens. The majority of stakeholders must approve a proposal for it to pass. The majority is defined differently depending on the DAO’s rules.
The advantage of DAOs vs. a traditional organization is the level of trustworthiness. Instead of needing to trust the people running the business, you only have to trust the code. The code is publicly available and verifiable to all members. Any action that the DAO takes has to be approved by the community. This allows everyone to contribute to decision-making. The voting system and instated rules provide an environment to more easily settle disputes. Additionally, since there is no hierarchy, people can feel comfortable voicing more innovative ideas.
#3 DeFi
DeFi stands for decentralized finance and it is essentially another type of application built via the blockchain. The goal is to provide a new financial system, one that does not rely on banks or exchanges. Instead, these financial services run on smart contracts and are typically built on the Ethereum network.
Similar to DAOs, DeFi relies on programmed rules in the code and therefore provides an element of trust and transparency. DeFi lending platforms are highly efficient and due to a lack of a middleman, such as a bank managing the system, you avoid the costs of traditional banks. This means DeFi lending platforms can offer much higher interest.
Some examples of what you can do with DeFi are: exchange tokens, crowdfund projects, and earn yield. Read more about DeFi here.
#4 NFTs
Web3 is run on tokens and there are two types of tokens:
Fungible tokens: interchangeable, divisible (e.g. US dollar, bitcoin)
Non-fungible tokens (NFT): unique, non-replicable (e.g. artwork, domain name)
In case you haven’t noticed a pattern above, NFTs are also powered by the Ethereum blockchain. Since these are run via smart contracts, it’s easy to tell who is the owner(s) of a particular NFT.
One popular use case of NFTs is digital artwork. This has allowed artists a means to create scarcity around their work. Digital artwork has historically been much easier to replicate than physical pieces of art, due to the fact people can copy and paste images on the internet. If an artist created a piece of digital art and released it on the internet, subsequently, an infinite number of versions could be floating around. NFTs provide a way for ownership of the artwork to be permanent and transparent.
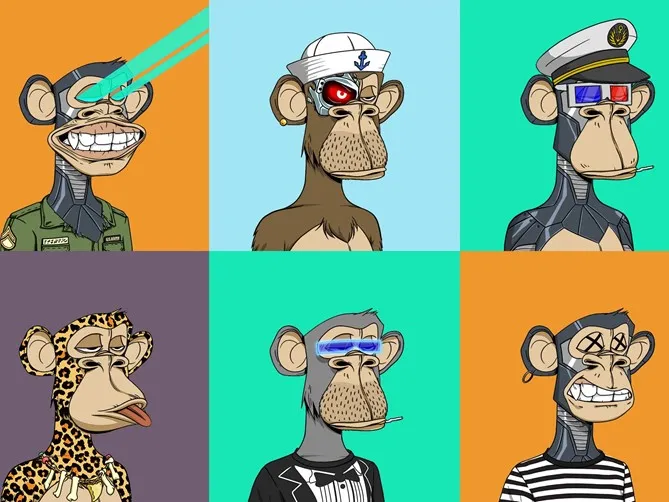

Bored Ape Yacht Club is a collection of 10,000 algorithmically generated unique avatars.
NFTs can also expand to sports, music, and many other industries. Aside from the potential for NFT owners to make huge profits or own items that appreciate, there are other non-monetary motivated advantages to NFTs. For example, you can buy an NFT to support a cause, as funds from NFTs can be donated to charities. The Bored Ape community was able to raise $1 million for animal shelters through sales of their digital artwork.
Another huge aspect of NFTs and Web3 is the power of community. Common interests and co-creation bring people together, and NFTs have the power to propel this innately human motivation at higher rates than ever before.
Why is Web3 important for Designers?
In this era of Web3, users are empowered more than ever to take control and ownership over their digital lives. With this ownership comes newfound responsibility for users. Given there are inevitable faults within any system, it is our responsibility to ensure that the experience is met with a level of ease and trustworthiness.
Blockchain technology is fueling this creator economy. Those creators and consumers are our users, and most likely many of us will be designing for these aforementioned applications one day. More and more tools are being built to give users the environment to take back control of the content they interact with.
As Designers and architects of the front-end UI, we must understand where the future of technology is headed, so that we can create evermore secure, efficient, and intuitive front-end systems that align with this unprecedented ownership.
You might also like…
How to reach me
© 2024 Taylor Green. All Rights Reserved.
Follow
taylorgreen.work@gmail.com